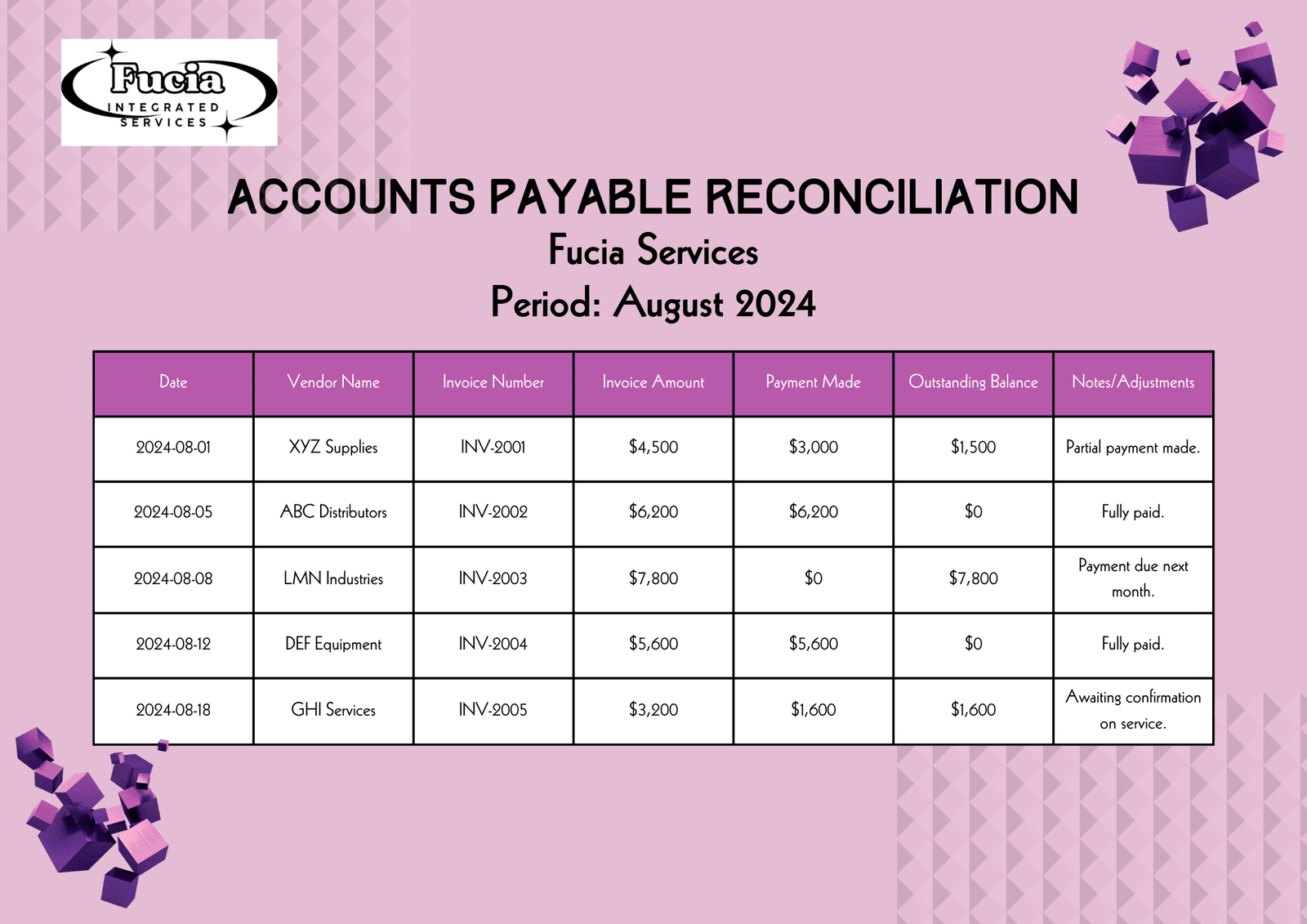
Vendor management is a critical aspect of supply chain management and procurement, encompassing a range of activities aimed at establishing and maintaining positive relationships with suppliers. Effective vendor management ensures that businesses can maximize value from their vendor relationships while minimizing risks and costs. Here’s an extensive overview of vendor management, covering its importance, key components, processes, best practices, and challenges.
Importance of Vendor Management
Key Components of Vendor Management
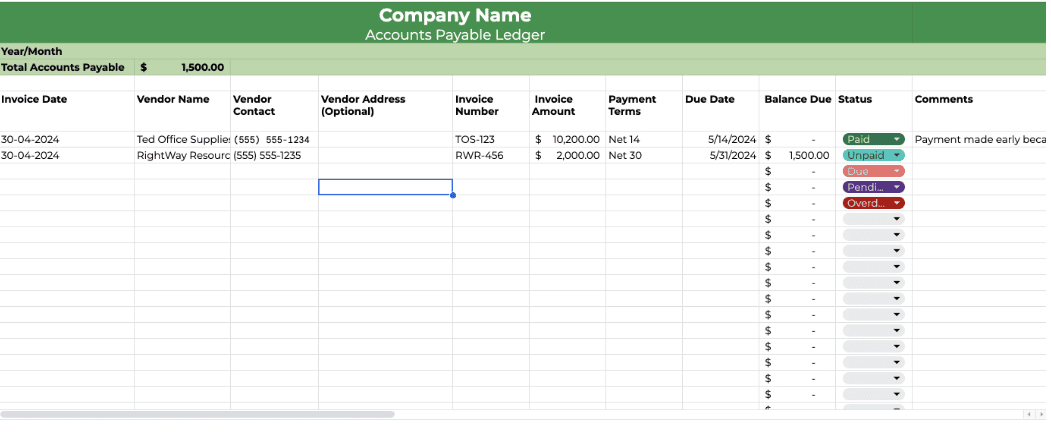
Vendor Management Process
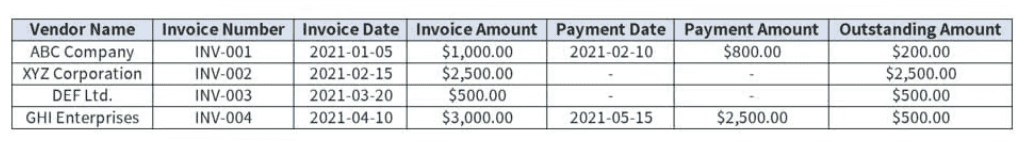
Best Practices in Vendor Management

Develop Clear Criteria: Establish criteria for vendor selection and evaluation to ensure consistency and fairness.
Challenges in Vendor Management

Conclusion

Vendor management is essential for organizations looking to optimize their supply chains and enhance their competitiveness. By establishing effective vendor management practices, businesses can improve quality, reduce costs, and foster strong partnerships that drive innovation and growth. Continuous evaluation and adaptation of vendor management strategies will ensure that organizations can respond effectively to changing market conditions and maintain a robust supply chain.
