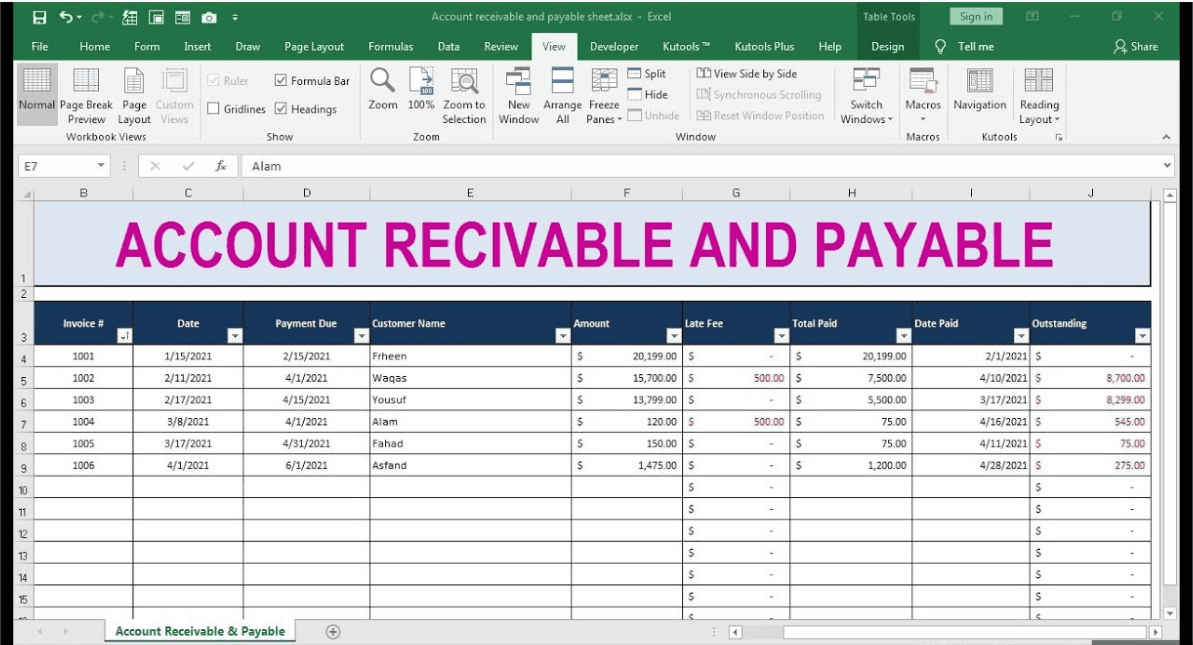
Accounts receivable (AR) reconciliation is a critical process for businesses, ensuring that the financial records accurately reflect the amounts owed by customers. This reconciliation helps maintain the integrity of financial statements, aids in cash flow management, and supports effective credit control.
What is Accounts Receivable Reconciliation?

Accounts receivable reconciliation is the process of comparing and matching the amounts recorded in a company’s financial records against the corresponding records provided by customers. This involves verifying that the accounts receivable balance in the general ledger matches the accounts receivable sub-ledger and customer statements.
Why is Reconciliation Important?

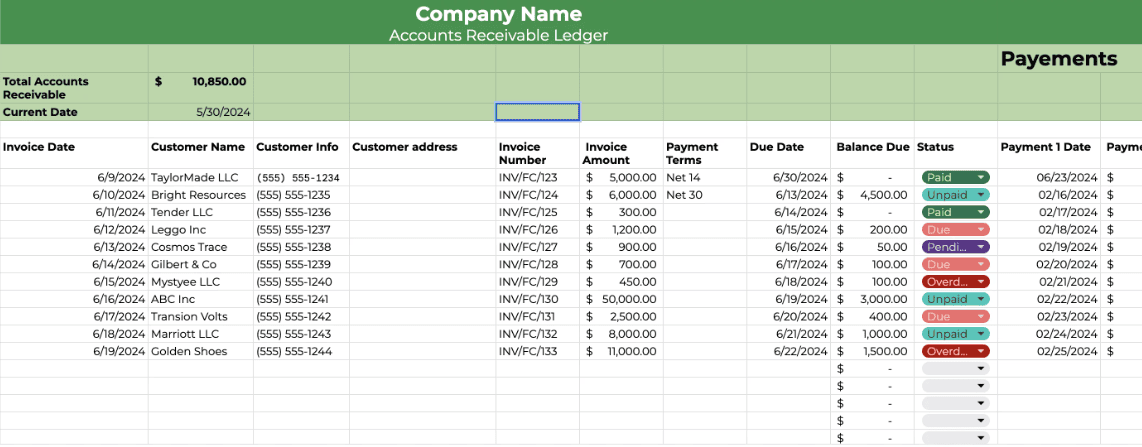
Steps in the Reconciliation Process
1. Gather Necessary Documents: Collect the accounts receivable aging report, customer statements, and any relevant invoices or payment records.

Best Practices for Effective Reconciliation
Conclusion
Accounts receivable reconciliation is an essential aspect of financial management that helps businesses maintain accuracy in their accounting records, improve cash flow, and enhance customer relationships. By following a systematic approach and implementing best practices, organizations can ensure their accounts receivable processes are effective and efficient, ultimately contributing to their financial health and success.
